RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew for IIS
V7.1.0
RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew for IIS runs as a Windows Service in a Windows hosting machine. The Windows Service will run every seven (7) days to automatically renew and save SSL/TLS certificates from a user’s subscription in the RCL SSL Portal to the Windows hosting machine.
Certificates will be automatically saved to the Local Machine certificate store in the Personal folder. Certificates will also be automatically bound to the IIS Web Server on the hosting machine.
Before you can use RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew, you must have already created your certificate(s) in the RCL SSL Portal using the Azure DNS or Azure DNS SAN option. The certificate(s) that you would like to install must be specified in your configuration of RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew.
Automatically Renew SSL/TLS Certificates
You can use RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew for IIS to automatically renew SSL/TLS certificates created in the RCL SSL Portal using the the following creation options :
Install RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew for IIS
If you have an older version of the RCL DNS AutoRenew for IIS installed in your hosting machine, you should delete it and install the new service.
Download the Files
-
The Windows Service files (
dns-autorenew-iis-win-xx) are available in the GitHub Project page in the Releases section: -
Download the zip file with bitness :
to match the Windows bitness of your hosting machine
-
Extract the zip file to a folder on your Windows hosting machine after it is downloaded
Configure the Service
Register an AAD Application
An Azure Active Directory (AAD) application must be registered to obtain permission to access a user’s Azure resources (DNS Zone).
Please refer to the following link to register an AAD application:
Set Access Control for the AAD Application
Access control must be set for the AAD application to access resources (DNS Zone) in a user’s Azure subscription. Please refer to the following link to set access control :
Get the AAD Application Credentials
To obtain the following credentials from the AAD application:
- ClientId
- ClientSecret
- TenantId
follow the instructions in this link :
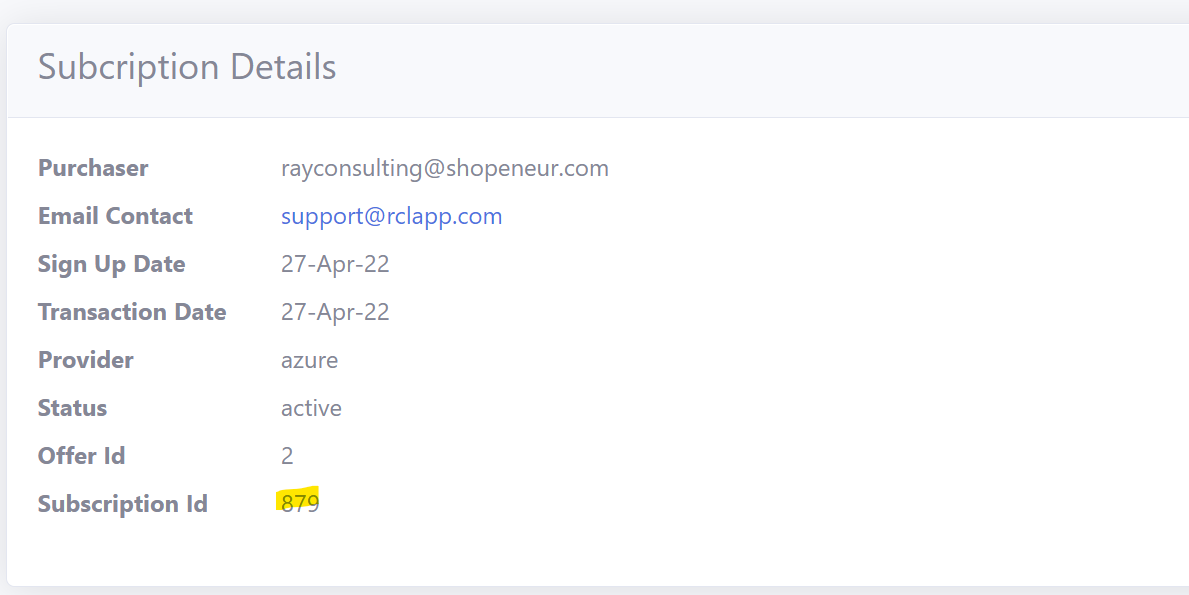
Get the SubscriptionId
Get the Subscription Id in the RCL SSL Portal.
- Scroll down and copy the ‘Subscription Id’
Register the AAD Application’s Client Id in the RCL SSL Portal
The AAD Application must be associated with a user’s RCL SSL subscription. This is achieved by registering the AAD Application’s Client Id in the RCL SSL Portal.
To add the AAD Application’s Client Id to the portal, please follow the instructions in this link :
Add the Configuration variables
-
In the folder containing the files for the Windows Service that you extracted, find and open the appsettings.json file
-
Add the credentials for the AAD Application and SubscriptionId in the RCLSDK section :
- ClientId
- ClientSecret
- TenantId
- SubscriptionId
"RCLSDK": {
"ApiBaseUrl": "https://rclapi.azure-api.net/v2",
"SourceApplication": "RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew IIS",
"ClientId": "23568fghjrtr3",
"ClientSecret": "7466rggvvdggdff",
"TenantId": "1103984664",
"SubscriptionId": "890"
}
-
In the CertificateBot section, set a folder path to save the SSL/TLS certificates. Recommended path : C:/ssl
- SaveCertificatePath
-
Note : when setting the folder path , use forward slashes(
/) in the path name, eg.C:/ssl. Failure to do this will result in inability to run the windows service. -
Create the folder in the hosting machine and ensure it has read/write permissions so that the certificates can be saved to it.
-
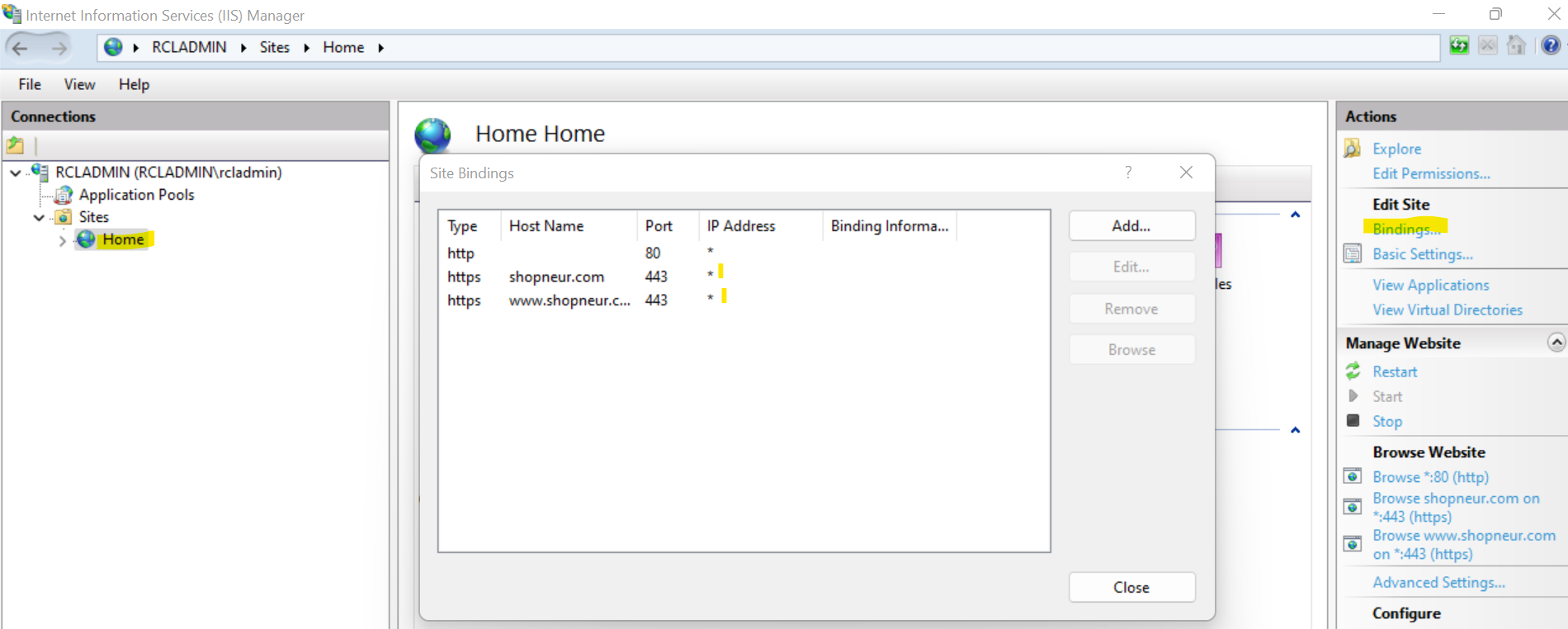
Configure the site bindings for each website that you want to bind a SSL/TLS certificate. You can have a single or multiple bindings.
- IISBindings
-
Example of multiple bindings :
"IISBindings": [
{
"siteName":"Home",
"ip":"*",
"port":"443",
"host":"shopneur.com",
"certificateName":"shopeneur.com,*.shopeneur.com"
},
{
"siteName":"Home",
"ip":"*",
"port":"443",
"host":"www.shopneur.com",
"certificateName":"shopeneur.com,*.shopeneur.com"
},
{
"siteName":"Fabricam",
"ip":"*",
"port":"443",
"host":"fabricam.com",
"certificateName":"fabricam.com"
},
{
"siteName":"Contoso",
"ip":"*",
"port":"443",
"host":"contoso.com",
"certificateName":"contoso.com"
}
]
- Example of a single binding :
"IISBindings": [
{
"siteName":"Home",
"ip":"*",
"port":"443",
"host":"shopneur.com",
"certificateName":"shopeneur.com"
}
]
- siteName - this is the Site name of the IIS website
- ip - this is the IP Address of the IIS website (you can use any (
*)) - port - the is the Port number of the IIS website (you can use
443) - host - the the Host Name assigned to the IIS website
- certificateName - this is the name of the certificate in the RCL SSL Portal to be installed in the IIS website
The image above illustrates a site hosted in IIS named ‘Home’ with multiple bindings. The site is bound to a naked apex domain, ‘shopeneur.com’, and a sub-domain ‘www.shopeneur.com’. The website can be accessed publicly on the web with either of these domains. The site uses the same multi-domain SAN certificate named : ‘shopeneur.com,*.shopeneur.com’ to provide SSL/TLS for both the domains.
Example of a configured appsettings.json file
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
},
"EventLog": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
}
},
"RCLSDK": {
"ApiBaseUrl": "https://rclapi.azure-api.net/v2",
"SourceApplication": "RCL SSL DNS AutoRenew IIS",
"ClientId": "23568fghjrtr3",
"ClientSecret": "7466rggvvdggdff",
"TenantId": "1103984664",
"SubscriptionId": "890"
},
"CertificateBot": {
"SaveCertificatePath": "C:/ssl",
"IISBindings": [
{
"siteName":"Home",
"ip":"*",
"port":"443",
"host":"shopneur.com",
"certificateName":"shopeneur.com,*.shopeneur.com"
},
{
"siteName":"Home",
"ip":"*",
"port":"443",
"host":"www.shopneur.com",
"certificateName":"shopeneur.com,*.shopeneur.com"
}
]
}
}
- Save the appsettings.json file when you are done.
Create the Windows Service
-
Open a Command Prompt in the Windows hosting machine as an Administrator
-
Run the following command to install the Windows Service. Replace the < file-path > placeholder with the actual path where your windows service zip files were extracted
sc.exe create DNSAutoRenewIIS binpath= <file-path>\RCL.SSL.DNS.AutoRenew.IIS.exe
Allow the Service through Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Microsoft Defender Antivirus may block the service. You must add the folder that you stored the service files to the Exclusions list in Microsoft Defender Antivirus Scans
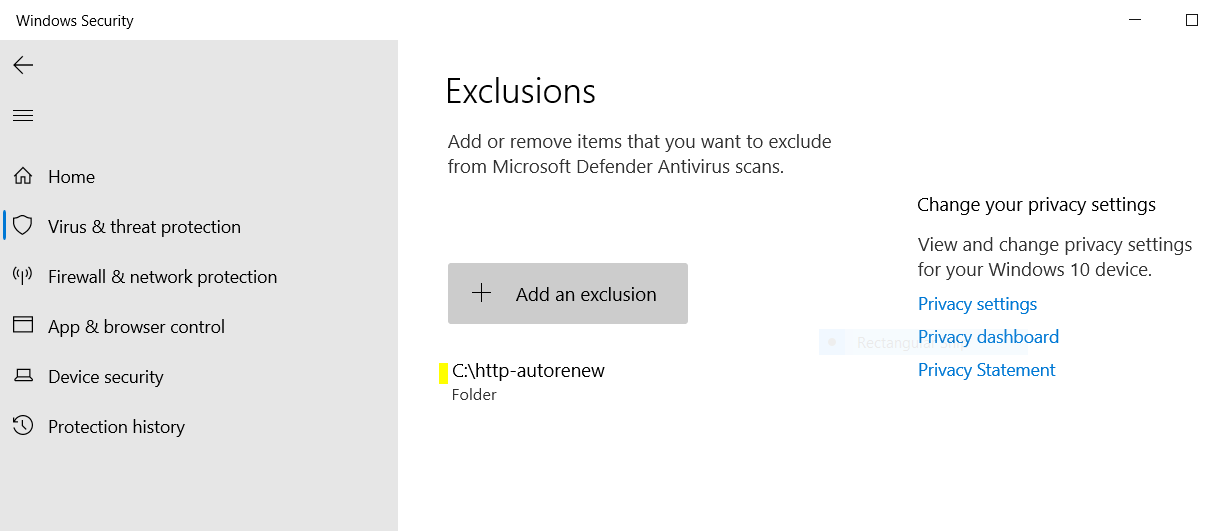
Alternatively, you can run a custom antivirus scan on the folder before you run the service.
Starting the Service
- After the service is installed, open Services in Windows, look for the
DNSAutoRenewIISservice and Start the service
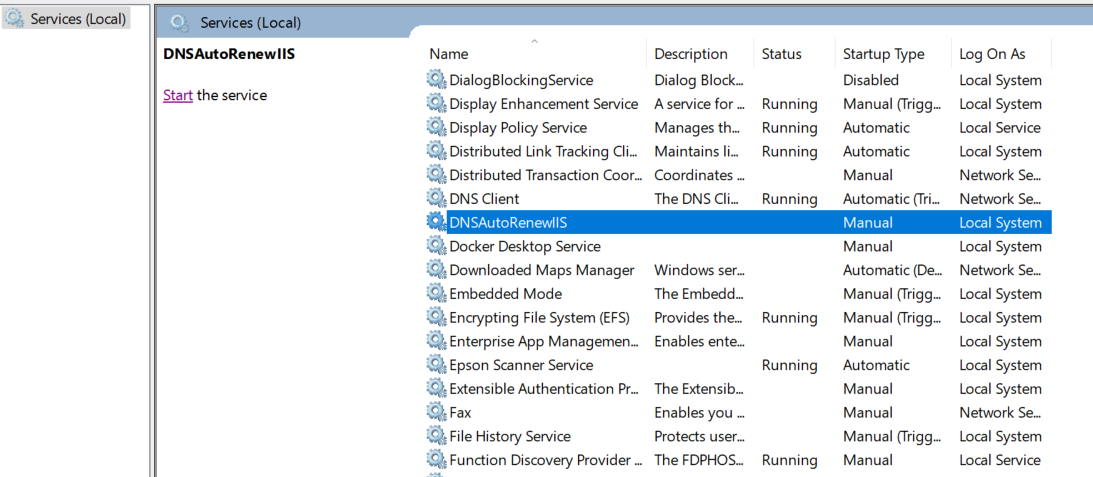
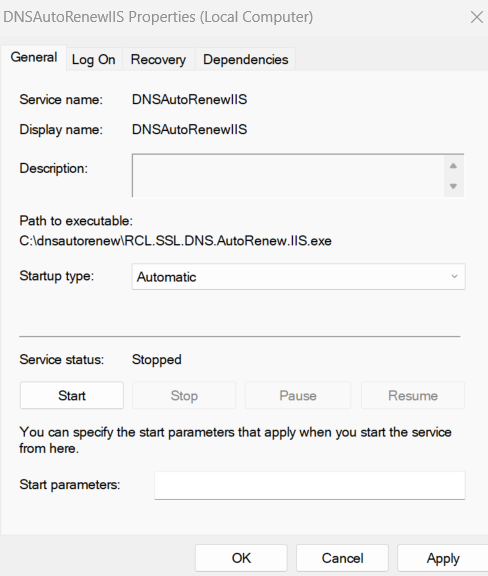
- Set the Properties of the service to start automatically when the hosting machine starts
View the Event Logs
- Open Event Viewer, under ‘Windows Logs > Application’, look for the
RCL.SSL.CertificateBot.IISevents
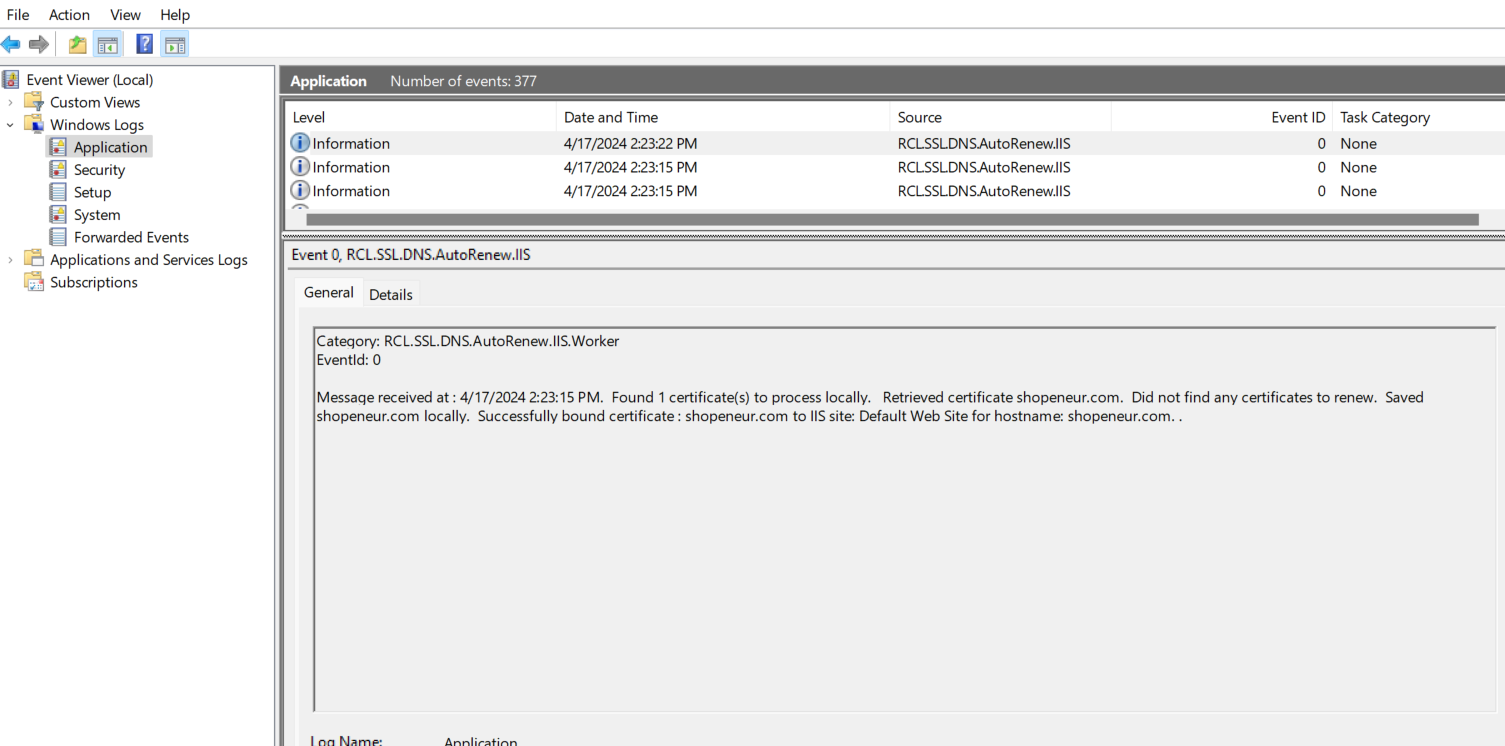
-
Ensure that there are no error events for the service. If there are error events, the service is misconfigured and will not function
-
Each time a certificate is downloaded and saved in the server or a certificate is scheduled for renewal, a log will be written
-
The service will run every seven (7) days to automatically renew certificates in the IIS web server
Fixing Errors
If you encounter error events for the service in the Event Viewer, please stop the service and delete it completely.
Ensure the appsettings configuration is correct for the AAD Application and the certificate save path settings point to a folder that exists.
Fix any other errors that are reported. Then, re-install and restart the service.
Deleting the Windows Service
If you need to remove the Windows Service for any reason, first stop the service, then run the command to delete the service
sc.exe delete DNSAutoRenewIIS
Updating the Service
If you need to update the service to include other IIS bindings and certificates, follow these steps:
- Stop the service and delete it
- Change the
appsettings.jsonfile to include updated IIS bindings and certificates - Re-create the service and start it
Reset the Service
If you need to reset the service because of a error or corrupted certificate renewal, follow these steps :
- Stop the service and delete it
- Delete all certificates and their folders in the directory in which certificates are saved
- Re-create the service and start it
Manually Testing Certificate Renewal
Force Certificate Expiration
In order to manually test certificate renewal, you must first force certificate expiration in the RCL SSL Portal.
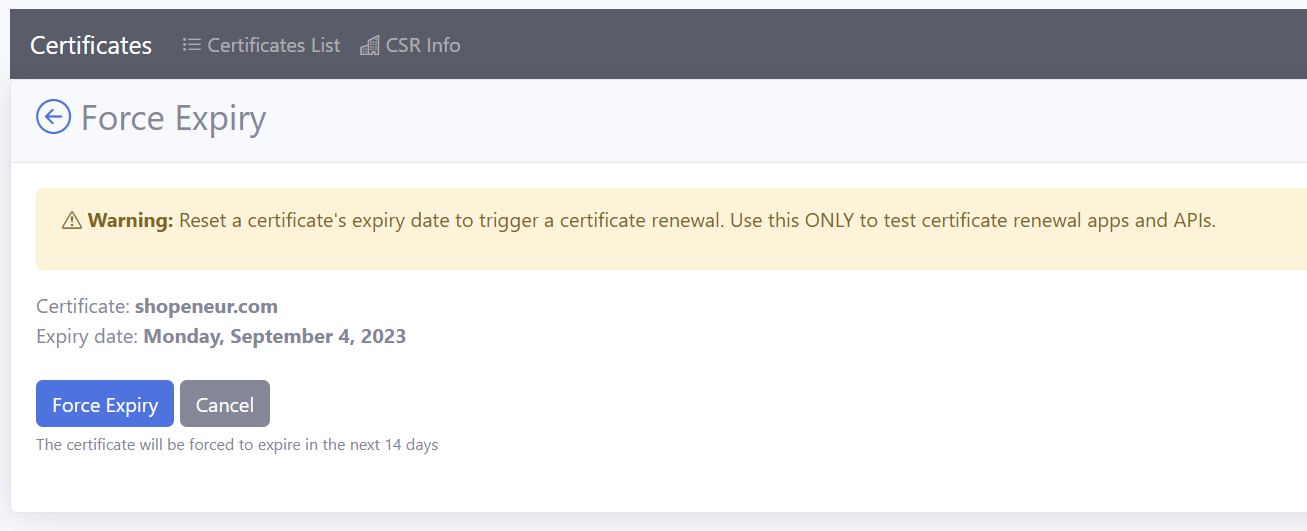
-
In the RCL SSL Portal, click on the SSL/TLS Certificate > Certificates List link in the side menu
-
In the certificates list, click the Manage > Force Expiry link
-
In the
Force Expirypage, click the Force Expiry button -
The certificate will be forced to expire in the next 14 days
Testing Renewal
-
Re-start the service to trigger the certificate renewal
-
Open Event Viewer, under ‘Windows Logs > Application’, look for the
RCL.SSL.HTTP.AutoRenew.IISevents -
Ensure that the certificate has been scheduled for renewal
-
Wait for 15 mins , then, re-start the services to save the certificate to the local machine and bind it to the IIS Web Server
-
Check that the certificate(s) are bound to the IIS website(s)
-
Once this test passes, the service will run automatically every seven days to renew certificate(s) and bind them to the IIS website(s)